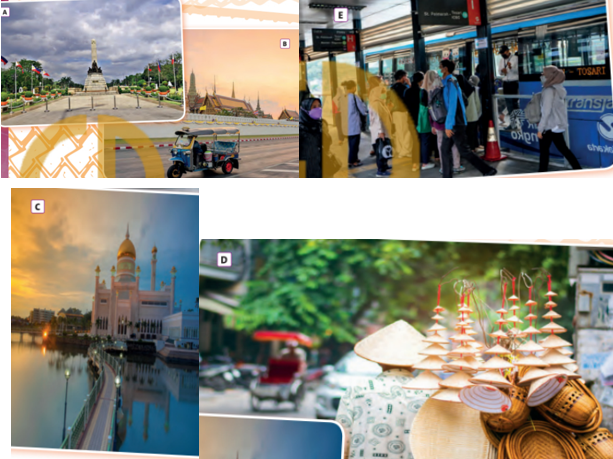
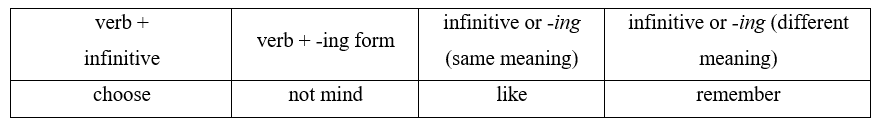
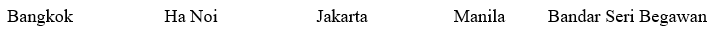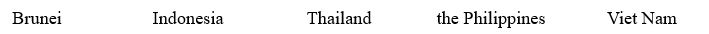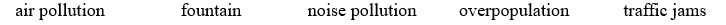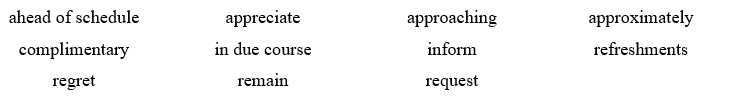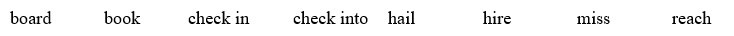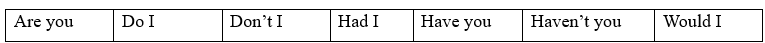INTRODUCTION
Bài tập Introduction
UNIT 1. GENERATIONS
Bài tập Unit 1
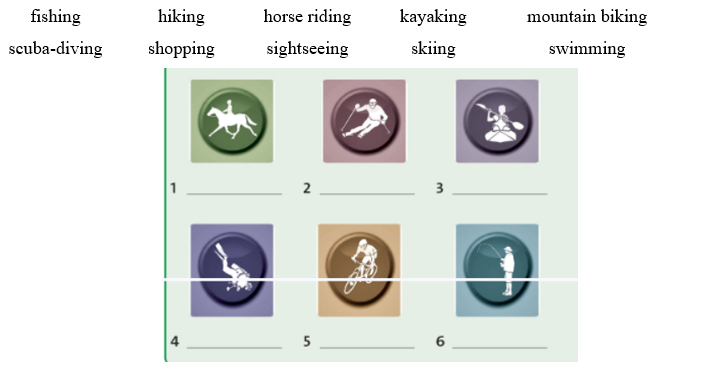
UNIT 2. LEISURE TIME
Bài tập Unit 2
UNIT 3. SUSTAINABLE HEALTH
Bài tập Unit 3
UNIT 4. HOME
Bài tập Unit 4
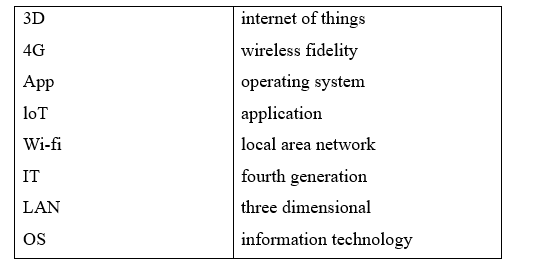
UNIT 5. TECHNOLOGY
Bài tập Unit 5
UNIT 6. HI-FLYERS
Bài tập Unit 6
UNIT 7. ARTISTS
Bài tập Unit 7
UNIT 8. CITIES
Bài tập Unit 8
REVIEW
Bài tập Review
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 8. Cities Friends Global
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 8 Friends Global
101 câu hỏi
Tự luận