UNIT 1. FAMILY LIFE
Bài tập Unit 1
UNIT 2. HUMANS AND THE ENVIRONMENT
Bài tập Unit 2
UNIT 3. MUSIC
Bài tập Unit 3
UNIT 4. FOR A BETTER COMMUNITY
Bài tập Unit 4
UNIT 5. INVENTIONS
Bài tập Unit 5
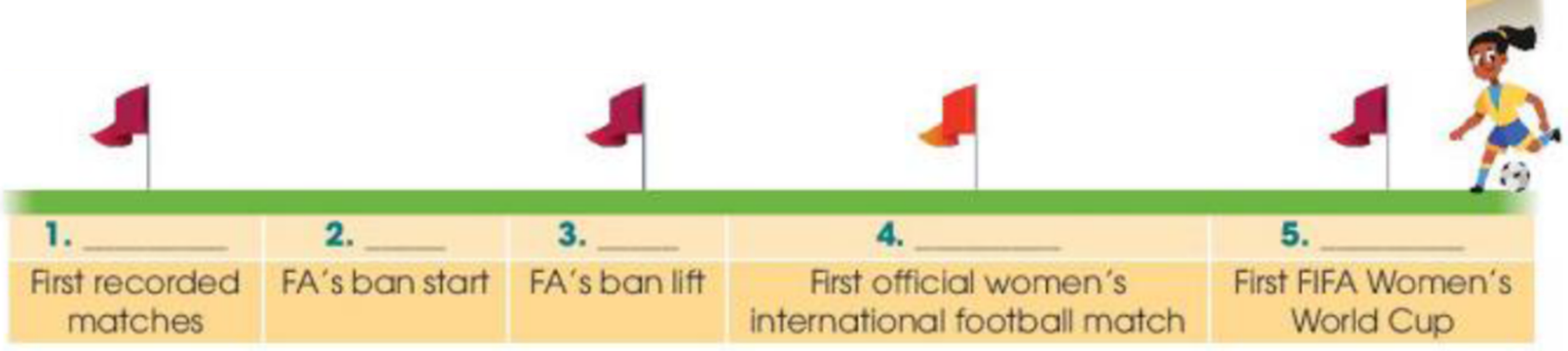
UNIT 6. GENDER EQUALITY
Bài tập Unit 6
UNIT 7. VIET NAM AND INTERNATIONAL ORGANISATIONS
Bài tập Unit 7
UNIT 8. NEW WAYS TO LEARN
Bài tập Unit 8
UNIT 9. PROTECTING THE ENVIRONMENT
Bài tập Unit 9
UNIT 10. ECOTOURISM
Bài tập Unit 10
REVIEW
Bài tập Review
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 6. Gender equality Global Success
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 6 Global Success
48 câu hỏi
Tự luận