Giải SGK, SBT Unit 5. Living environment Right on!
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 5. Living environment Right on!
1. Listen and repeat. Complete the sentences with the word/phrases from the list.
(Nghe và lặp lại. Hoàn thành câu với từ/cụm từ trong danh sách.)
|
schools and universities |
job opportunities |
healthcare system |
cost of living |
|
facilities |
public services |
fresh food |
friendly people |
1. Most cities have a good _______ with lots of hospitals and doctor’s offices.
2. When we moved to the countryside, we met a lot of _______.
3. You can have a good career in the city because there are more _______ there.
4. In urban areas, there are a lot of _______ like roads and bridges.
5. People in rural areas have lots of space to grow their own _______.
6. The government spent a lot of money providing rural people with _______, like schools and hospitals.
7. Some people prefer living in the countryside because the _______ there is low.
8. There are many _______ in urban areas, so it is easy to get a good education there.
Comparative - as … as - not as/so … as
|
We use the comparative to compare one person/thing with another.
Facilities in the city are more modern than those in the countryside. Vehicles in urban areas move more slowly than vehicles in rural areas. Irregular adjectives/adverbs: good/well -> better, bad/badly -> worse, far -> farther/further, little -> less, much/many -> more. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
We use as + adjective/adverb + as to say that two people/things are similar in some ways. My new friends treat me as nicely as my old friends did. We use not as/so + adjective/adverb + as to say that two people/things are different in some ways. The air in the city isn’t as/so fresh as the air in the countryside. |
Tạm dịch:
|
Chúng ta sử dụng so sánh hơn để so sánh người/vật này với người/vật khác.
Cơ sở vật chất ở thành phố hiện đại hơn ở nông thôn. Xe ở thành thị di chuyển chậm hơn xe ở nông thôn. Tính từ/trạng từ bất quy tắc: tốt/tốt -> tốt hơn, xấu/xấu -> tệ hơn, xa -> xa hơn/xa hơn, ít -> ít hơn, nhiều/nhiều -> nhiều hơn. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Chúng ta sử dụng as + tính từ/trạng từ + as để nói rằng hai người/sự vật giống nhau ở một khía cạnh nào đó. Những người bạn mới của tôi đối xử với tôi cũng tử tế như những người bạn cũ của tôi đã làm. Chúng ta dùng not as/so + tính từ/trạng từ + as để nói rằng hai người/sự vật khác nhau ở một khía cạnh nào đó. Không khí ở thành phố không trong lành như không khí ở nông thôn. |
1. Put the adjectives/adverbs into their comparative forms.
(Đặt tính từ/trạng từ ở dạng so sánh hơn.)
1. Julie often finishes maths exercises _______ (fast) than me.
2. Life in the city is _______ (convenient) than life in the countryside.
3. Urban people often dress _______ (fashionably) than rural people do.
4. Our new neighbours are _______ (helpful) than our old neighbours.
5. Traffic in the morning is _______ (heavy) than traffic in the afternoon.
6. We grow food _______ (cheaply) in rural areas than we do in urban areas.
Superlative
|
We use the superlative to compare one thing/person with others in the same group.
This is the tallest building in my country. The electric buses run the most quickly of all the buses in the town. Irregular adjectives/adverbs: good/well -> the best, bad/badly -> the worst, far -> the farthest/furthest, little -> the least, much/many-> the most. |
Tạm dịch:
|
Chúng ta sử dụng so sánh nhất để so sánh một vật/người với những vật/người khác trong cùng một nhóm.
Đây là tòa nhà cao nhất ở đất nước tôi Xe buýt điện chạy nhanh nhất trong số tất cả các xe buýt trong thị trấn. Tính từ/trạng từ bất quy tắc: tốt/tốt -> tốt nhất, xấu/xấu -> tệ nhất, xa -> xa nhất/xa nhất, ít -> ít nhất, nhiều/nhiều-> nhất. |
4. Put the adjectives/adverbs into their superlative forms.
(Đặt tính từ/trạng từ ở dạng so sánh nhất.)
1. Hồ Chí Minh City is _______ (crowded) city in Việt Nam.
2. Zurich is one of _______ (little) polluted cities in Europe.
3. Denmark is one of _______ (clean) countries in the world.
4. The population of this city grows _______ (rapidly) of all cities in the country.
5. He joins the volunteer activities _______ (actively) of all students in my class.
3. Listen to two people talking about how to improve their living environment and fill in the gaps (1-5). Write NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS for each gap.
(Nghe hai người nói về cách cải thiện môi trường sống và lấp đầy những khoảng trống (1-5). Viết KHÔNG QUÁ HAI TỪ cho mỗi chỗ trống.)
|
Clean transport |
- (1) _______ / ride a bicycle - use (2) _______ |
|
Green spaces |
- (3) _______ in the parks |
|
Community service |
- do (4) _______for the elderly - pick up rubbish - (5) _______ at the animal shelters |
Bài nghe:
Peter: Hi Samantha, I want to help improve our living environment. Do you have any ideas?
Samantha: Oh, hi Peter,there are lots of things we can do to make our community a better place. Clean transport is an example.
Peter: That's right, we can walk or ride a bicycle instead of driving.
Samantha: We can use public transport too, but that's another form of clean transport.
Peter: Exactly. What else can we do to improve the living environment of our community?
Samantha: We can make green spaces more beautiful. For example, we can plant trees in the parks.
Peter: That's a great plan. Do you have any other ideas?
Samantha: Everyone can do that part and do community service. There are lots of programs that need volunteers.
Peter: That's true. We can do shopping for the elderly or pick up trash in the parks and on the beaches.
Samantha: Those are wonderful ways to volunteer. You can also help at the animal shelter. It's a good way to do community service.
Peter: I will find a program that needs help and sign up today.
Samantha: I will sign up, too.
Tạm dịch:
Peter: Xin chào Samantha, tôi muốn giúp cải thiện môi trường sống của chúng ta. Bạn có bất cứ ý tưởng?
Samantha: Ồ, xin chào Peter, có rất nhiều điều chúng ta có thể làm để biến cộng đồng của mình thành một nơi tốt đẹp hơn. Giao thông sạch là một ví dụ.
Peter: Đúng rồi, chúng ta có thể đi bộ hoặc đi xe đạp thay vì lái xe.
Samantha: Chúng ta cũng có thể sử dụng phương tiện giao thông công cộng, nhưng đó là một hình thức giao thông sạch khác.
Peter: Chính xác. Chúng ta có thể làm gì khác để cải thiện môi trường sống của cộng đồng?
Samantha: Chúng ta có thể làm cho không gian xanh trở nên đẹp hơn. Ví dụ, chúng ta có thể trồng cây trong công viên.
Peter: Đó là một kế hoạch tuyệt vời. Bạn có bất cứ ý tưởng khác?
Samantha: Mọi người đều có thể làm phần việc đó và phục vụ cộng đồng. Có rất nhiều chương trình cần tình nguyện viên.
Peter: Đúng vậy. Chúng ta có thể đi mua sắm cho người già hoặc nhặt rác ở công viên và trên bãi biển.
Samantha: Đó là những cách tuyệt vời để làm tình nguyện. Bạn cũng có thể giúp đỡ tại nơi trú ẩn động vật. Đó là một cách tốt để làm dịch vụ cộng đồng.
Peter: Tôi sẽ tìm một chương trình cần trợ giúp và đăng ký ngay hôm nay.
Samantha: Tôi cũng sẽ đăng ký.
1. Read the dialogue and fill in the gaps (1-4) with the sentences (A-D). Listen and check.
(Đọc đoạn hội thoại và điền vào chỗ trống (1-4) bằng các câu (A-D). Nghe và kiểm tra.)
|
A. For example, we can use clean transport to improve air quality. B. What else can we do to improve our living environment? C. Do you have any idea? D. That’s a great plan! |
Amy: I want to help improve our living environment. (1) ________________________________
Conner: There are lots of things we can do to make our community better. (2) ________________________________
Amy: That’s right. We can use better waste solutions like recycling, too.
Conner: Exactly! (3) ________________________________
Amy: We can also ask city planners to provide more low-cost housing to people.
Conner: (4) ________________________________. Do you have any other ideas?
Amy: We can also do community service. There are lots of programmers that need volunteers.
Conner: That's true. We can do the shopping for the elderly.
Amy: Good idea! After school today, I’ll ask some of my elderly neighbours if they need help.
Conner: Great! I’ll come with you.
Bài nghe:
Amy: I want to help improve our living environment. Do you have any idea?
Conner: There are lots of things we can do to make our community better. For example, we can use clean transport to improve air quality.
Amy: That’s right. We can use better waste solutions like recycling, too.
Conner: Exactly! What else can we do to improve our living environment?
Amy: We can also ask city planners to provide more low-cost housing to people.
Conner: That’s a great plan! Do you have any other ideas?
Amy: We can also do community service. There are lots of programmers that need volunteers.
Conner: That's true. We can do the shopping for the elderly.
Amy: Good idea! After school today, I’ll ask some of my elderly neighbours if they need help.
Conner: Great! I’ll come with you.
3. Act out a similar dialogue. Use the dialogue in Exercise 1 as a model and the ideas below and/or your own ideas.
(Diễn lại một đoạn hội thoại tương tự. Sử dụng đoạn hội thoại trong Bài tập 1 làm mẫu và các ý dưới đây và/hoặc ý của riêng bạn.)
|
- ask city planners to build facilities (roads, bridges) - plant trees to improve air quality - start a community garden to provide fresh food to people - do community service (pick up rubbish, start a recycling programme) |
Listen and mark the sentences ⇗ (rising intonation) or ⇘ (falling intonation). Practice saying them with your partner.
(Nghe và đánh dấu các câu ä (ngữ điệu lên) hoặc æ (ngữ điệu xuống). Thực hành nói chúng với đối tác của bạn.)
|
1. Do you have any idea? |
|
|
2. I want to help improve your living environment. |
|
|
3. What else can we do to improve our living environment? |
|
|
4. That’s a great plan! |
|
|
5. I’ll come with you. |
|
|
6. There are lots of things we can do to make our community a better place. |
|
5e. Grammar
Defining relative clauses
|
We use a relative clause to modify the noun before it. A defining relative clause gives important information to define the noun it modifies. This information is essential to the meaning of the sentence. - We use relative pronouns (who, whom, which, that and whose) to introduce defining relative clauses. When the relative pronoun is the object of the defining clause, it can be omitted. - We don’t use a comma between the defining relative clause and the noun. who/that (people, subject) The people who/that live in the areas with green spaces are often healthy. whom/that (people, object) The city planners (whom/that) we were waiting for are arriving soon. which/that (things, subject/object) I prefer living in places which/that have good facilities and public services. The city (which/that) I’m leaving for is very clean and tidy. whose (people/things, possessive adjective) People like living in the cities whose waste solutions are effective. The scientist whose son is my classmate is giving a talk on TV. |
Tạm dịch:
|
Chúng ta sử dụng mệnh đề quan hệ để bổ nghĩa cho danh từ đứng trước nó. Mệnh đề quan hệ xác định cung cấp thông tin quan trọng để xác định danh từ mà nó bổ nghĩa. Thông tin này rất cần thiết cho ý nghĩa của câu. -- Chúng ta sử dụng đại từ quan hệ (who, who, which, that và who) để giới thiệu mệnh đề quan hệ xác định. Khi đại từ quan hệ là tân ngữ của mệnh đề xác định thì có thể lược bỏ nó. - Chúng ta không dùng dấu phẩy giữa mệnh đề quan hệ xác định và danh từ. ai/cái đó (người, chủ đề) who/that (người, đồ vật) Những người sống ở những khu vực có không gian xanh thường khỏe mạnh. whom/that (sự vật, chủ thể/đối tượng) Những người quy hoạch thành phố (ai/cái đó) mà chúng tôi đang chờ đợi sẽ sớm đến. which/that (cái gì, sự vật/đồ vật) Tôi thích sống ở những nơi có cơ sở vật chất và dịch vụ công cộng tốt. Thành phố (mà/đó) tôi sắp đến rất sạch sẽ và ngăn nắp. whose (người/vật, tính từ sở hữu) Mọi người thích sống ở những thành phố có giải pháp xử lý rác thải hiệu quả. Nhà khoa học có con trai là bạn cùng lớp của tôi đang thuyết trình trên TV. |
1. Fill in the gaps with who, whom, which, that and whose. Some sentences have two possible answers.
(Điền vào chỗ trống với who, whom, which, that và whose. Một số câu có thể có hai câu trả lời.)
1. The bus system _______ the city just developed is a type of clean transport.
2. The volunteers _______ job is to help the elderly are very helpful and energetic.
3. The students _______ are picking up rubbish at the park are my classmates.
4. The man _______ you spoke to in the park yesterday is an environmental scientist.
5. I want to buy a house in an area _______ has lots of green spaces.
Non-defining relative clauses
|
A non-defining relative clause give additional information to the noun it modifies. This information doesn’t define the noun and is not important to the meaning of the sentence. - We use relative pronouns (who, whom, which and whose) to introduce non-defining relative clauses. We cannot use that in non-defining relative clauses. The pronouns in non-defining clauses cannot be omitted. - There is a comma between the non-defining relative clause and the noun. John, who works as a city planner, is designing a new clean transport system. My best friend is Lily, whom you met in the environmental event yesterday. Those building, which the city built last year, provide low-cost housing options. My sister, whose new car runs on electricity, cares a lot about clean transport. |
Tạm dịch:
|
Mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định cung cấp thêm thông tin cho danh từ mà nó bổ nghĩa. Thông tin này không xác định danh từ và không quan trọng đối với ý nghĩa của câu. - Chúng ta sử dụng đại từ quan hệ (who, who, which và which) để giới thiệu mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định. Chúng ta không thể sử dụng điều đó trong mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định. Đại từ trong mệnh đề không xác định không được bỏ qua. - Giữa mệnh đề quan hệ không xác định và danh từ có dấu phẩy. John, người làm công việc quy hoạch thành phố, đang thiết kế một hệ thống giao thông sạch mới. Bạn thân nhất của tôi là Lily, người mà bạn đã gặp trong sự kiện môi trường ngày hôm qua. Những tòa nhà mà thành phố xây dựng năm ngoái cung cấp các lựa chọn nhà ở giá rẻ. Chị tôi có chiếc ô tô mới chạy bằng điện rất quan tâm đến phương tiện giao thông sạch. |
4. Fill in the gaps with who, whom, which, that and whose.
(Điền vào chỗ trống với who, whom, which, that và whose.)
1. Mr Nam is leaving for Hà Nội, _______ offers lots of education and job opportunities.
2. Air pollution, _______ can cause some diseases, is now a big problem in urban areas.
3. Bob, _______ we expected to win the competition, had an excellent performance.
4. Elizabeth, _______ is an animal nutritionist, takes care of animals at the zoo.
5. They are developing a new public transport system in my city, _______ traffic is very happy.
6. These waste solutions, _______ the city planners suggested, are going to make our neighbourhood cleaner.
3. Read the text again and answer the questions (1-5). Write Singapore or Sydney.
(Đọc lại đoạn văn và trả lời các câu hỏi (1-5). Viết Singapore hoặc Sydney.)
Which city …? (Thành phố nào…?)
|
1. makes it easy for people to walk or cycle |
_____________________________ |
|
2. make low-cost housing a priority |
_____________________________ |
|
3. doesn’t have a lot of rural areas |
_____________________________ |
|
4. offers a lot of electric charging stations |
_____________________________ |
|
5. has a building that uses eco-friendly energy |
_____________________________ |
1. Read the task and complete the table.
(Đọc bài và hoàn thành bảng.)
You read an article about the importance of green cities in the school magazine editor making suggestions for making your are greener (about 100-120 words). Include a greeting and the reason for writing, suggestions and expected results and a closing remark.
(Bạn đọc một bài viết về tầm quan trọng của thành phố xanh trên tạp chí của trường, biên tập viên đưa ra những gợi ý giúp bạn trở nên xanh hơn (khoảng 100-120 từ). Bao gồm lời chào và lý do viết bài, đề xuất, kết quả mong đợi và nhận xét kết thúc.)
|
Type of text (Loại văn bản) |
|
|
Readers (Độc giả) |
|
|
Topic (Chủ đề) |
|
|
Number of words (Số từ) |
|
|
What to include (Những gì cần bao gồm) |
|
2. Read the email. In which part (1-3) does Martha …?
(Đọc email. Ở phần nào (1-3) Martha…?)
|
a |
|
give suggestions and expected results (đưa ra gợi ý và kết quả mong đợi) |
|
b |
|
give a closing remark (đưa ra nhận xét kết thúc) |
|
c |
|
give a greeting and the reason for writing (chào hỏi và lý do viết thư) |
(1) To the Editor
I am writing to suggest some ways to make our area greener.
(2) Firstly, we should build more walking and cycling paths to encourage people to walk and cycle. In this way, we can reduce air pollution. Secondly, we can start a community garden to provide fresh food for everyone in our area. If we do this, we will all be healthier and happier. Lastly, tree-planting events can be a good idea. Then, we will have more green spaces for people to enjoy fresh air.
(3) I hope my suggestions will help.
Yours faithfully,
Martha Rawlings
want to do one day? Tell me about it in your comments.
6. Listen to an interview about eating a balanced diet. Decide if the statements (1-5) are R (right) or W (wrong).
(Nghe một cuộc phỏng vấn về việc ăn một chế độ ăn uống cân bằng. Quyết định xem các câu (1-5) là R (đúng) hay W (sai).)
|
1. Green buildings are green in colour. |
|
|
2. Green buildings are popular today. |
|
|
3. Green buildings use more water and energy than other buildings. |
|
|
4. We can use wood to build green buildings. |
|
|
5. It costs more to build green buildings than traditional buildings. |
|
Bài nghe:
MC: On the show this afternoon, green building expert Mark Thompson. Welcomes Mark.
Mark: Thank you for having me.
MC: What exactly is a green building? Are they green in color?
Mark: No, it's not about the color. Green buildings are better for the environment than other types of buildings; they are very popular today.
MC: Of course, we should construct green buildings because taking care of the environment is important, but do green buildings actually use fewer resources than other buildings?
Mark: Yes, they do. For instance, they use less water and less energy than other buildings. and we use resources that are more sustainable to build them right. We can use wood to build them instead of other materials.
MC: Are there any disadvantages to constructing more green buildings in our city?
Mark: Green buildings can be more expensive to construct than traditional buildings, but they cost less to run, so it's only a disadvantage at first. This means they lower our cost of living.
MC: I see it sounds like green buildings are very important. Thank you for speaking with us today.
Mark: You're welcome.
Tạm dịch:
MC: Trong chương trình chiều nay, chuyên gia công trình xanh Mark Thompson. Chào mừng Mark.
Mark: Cảm ơn vì đã mời tôi.
MC: Chính xác thì công trình xanh là gì? Chúng có màu xanh lục không?
Mark: Không, vấn đề không phải là màu sắc. Công trình xanh tốt cho môi trường hơn các loại công trình khác; chúng rất phổ biến ngày nay.
MC: Tất nhiên, chúng ta nên xây dựng các công trình xanh vì việc chăm sóc môi trường là quan trọng, nhưng liệu các công trình xanh có thực sự sử dụng ít tài nguyên hơn các công trình khác không?
Mark: Có, đúng vậy. Ví dụ, chúng sử dụng ít nước và ít năng lượng hơn các tòa nhà khác. và chúng tôi sử dụng các nguồn tài nguyên bền vững hơn để xây dựng chúng một cách đúng đắn. Chúng ta có thể sử dụng gỗ để xây dựng chúng thay vì các vật liệu khác.
MC: Có bất lợi nào khi xây dựng thêm nhiều công trình xanh ở thành phố của chúng ta không?
Mark: Xây dựng các tòa nhà xanh có thể tốn kém hơn so với các tòa nhà truyền thống, nhưng chi phí vận hành lại thấp hơn nên ban đầu, đây chỉ là một bất lợi. Điều này có nghĩa là họ giảm chi phí sinh hoạt của chúng tôi.
MC: Tôi thấy có vẻ như công trình xanh rất quan trọng. Cảm ơn bạn đã nói chuyện với chúng tôi ngày hôm nay.
Mark: Không có gì.
7. Read the blog entry and decide if the statements (1-5) are R (right), W (wrong) or DS (doesn’t say).
(Đọc mục blog và quyết định xem các câu (1-5) là R (đúng), W (sai) hay DS (không nói).)
Fred’s Blog
Hi readers! Today, I want to tell you about my new neighbourhood. I used to live in rural area. My family had a farm there for many years, but we moved to the city recently because there are lots of job opportunities for my parents here. Sometimes, I miss life in the countryside, but there are many great things about living in the city. Thee are fewer things to do in the countryside than in urban areas, so the city life keeps me busier than the farm life. I enjoy going to the cinema and other fun places with my new friends. The only thing I don’t like is the traffic. Luckily, the city has some cycling paths, so I ride my bike to school almost every day. Sometimes, I miss the beautiful scenery of the countryside, but the park near my new house is just as pretty as my old neighbourhood. It has even got a lake. What about your neighbourhood? Leave a comment below and say what it is like to live there. Bye for now!
|
1. Fred’s family used to live on a farm. |
|
|
2. Fred doesn’t miss the area that he lived in before. |
|
|
3. Fred’s life in the city is busier than his life in the rural area. |
|
|
4. Fred often goes to the cinema with his friends at the weekend. |
|
|
5. There is a park close to Fred’s new home. |
|
1. What is your ideal neighbourhood like? Think about streets, buildings, parks, transport and facilities. Draw a map of the area.
(Khu phố lý tưởng của bạn như thế nào? Hãy suy nghĩ về đường phố, tòa nhà, công viên, phương tiện giao thông và cơ sở vật chất. Vẽ bản đồ khu vực.)
|
green buildings |
facilities (roads, bridges) |
|
public transport |
green spaces (parks, gardens) |
|
electric charging stations |
public services (schools, hospitals, libraries) |
|
low-cost apartments |
urban farming (vertical farms, community garden) |

1. Match the words to make phrases. Then use the phrases to complete the sentences (1-7).
(Nối các từ để tạo thành cụm từ. Sau đó sử dụng các cụm từ để hoàn thành câu (1-7).)
|
1. friendly |
a. food |
|
2. job |
b. universities |
|
3. public |
c. opportunities |
|
4. cost of |
d. system |
|
5. schools and |
e. people |
|
6. healthcare |
f. living |
|
7. fresh |
g. services |
1. Mrs Evans eats _______ from her garden every day.
2. It’s expensive to live here. The _______ is always increasing.
3. Urban areas have lots of _______, like libraries and post offices.
4. There are lots of _______ in my village. We all know each other.
5. My country has a good _______ with lots of doctors and hospitals.
6. Christine moved to London for work because there are more _______ in the city.
7. Education is important to me, so I want ti live in a place with good _______.
Features of a living environment
1. Complete the headlines with the words from the list.
(Hoàn thành các tiêu đề bằng các từ trong danh sách.)
|
clean |
quality (x2) |
housing |
|
waste |
spaces |
community |
1. _______ TRANSPORT IMPROVES AIR _______
2. NEW GREEN _______ IN URBAN AREAS OFFER A SOLUTION
3. MAYOR ENCOURAGES _______ SERVICES TO HELP LOCAL SOCIETY
4. FACTORIES NEAR RIVER ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR POOR WATER _______
5. _______ SOLUTIONS PLAN KEY TO CONTROL LITTER POLLUTION
6. GOVERNMENT PLANS TO PROVIDE LOW-COST _______ FOR ALL POPULATION GROUPS
2. Complete the gaps with the correct verbs from the list.
(Điền vào chỗ trống với các động từ đúng trong danh sách.)
|
use (x2) |
improve |
do |
|
provide |
create |
GOOD LIVING ENVIRONMENT
All people have a right to a good living environment. Cities are creating better local environments for everyone by taking some actions. Shelter is a basic human right, and many cities (1) _______ low-cost housing so that people can afford a nice, safe place to live. They also (2) _______ green spaces for people to use for outdoor activities. Studies also show that green spaces make people in urban areas feel happier. In addition, green spaces also (3) _______ air quality in cities because trees and plants help to clean the air.
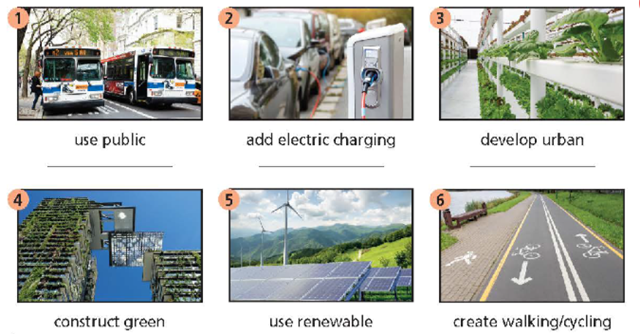
These are all great changes that our governments and councils are making, but we are also responsible for improving our living environment. We should (4) _______ clean transport instead of driving or taking a taxi. We also need to (5) _______ waste solutions like recycling bins. We can also (6) _______ community service, such as planting trees or helping our elderly neighbours. In this way, we all work together for a better community, city and world.
Discussing ways for improving the living environment
1. Match the sentences to make exchanges.
(Nối các câu để trao đổi.)
|
1. Do you have any ideas? |
a. Great! I’ll come with you. |
|
2. We can make the streets nicer. |
b. There are lots of things we can do. |
|
3. I’m going to join a volunteer club. |
c. That’s right. We can plant flowers. |
Pronunciation
4. Mark the sentences ⇗ (rising intonation) or ⇘ (falling intonation). Listen and check, then repeat.
(Đánh dấu câu ⇗ (ngữ điệu lên) hoặc ⇘ (ngữ điệu xuống). Nghe và kiểm tra, sau đó lặp lại.)
|
1. Do you have any idea? |
|
|
2. Good idea! |
|
|
3. What else can we do to improve our living environment? |
|
|
4. We can plant trees and flowers to improve air quality. |
|
|
5. I’m going to ask my classmates if they want to do this at the weekend. |
Ways to Make a City green
How can we improve the cities where we live in? Let’s find out.
- One of the best ways to improve cities is to add green spaces. Urban farming is popular in Paris, France, which is home to the world’s largest rooftop garden. People use it to grow fresh food for local restaurants and homes.
- Reducing the use of cars is also important. Cities like Auckland, New Zealand create safe paths which make walking a better choice than driving. Amsterdam in the Netherlands has over 500 kilometres of cycling paths.
- Constructing green buildings can also improve living environment. These buildings improve air quality both inside and outside. People get sick less often and can work better - they even sleep better at night because green buildings use natural light all day. Adelaide in Australia has got many green buildings.
- Clean transport is essential in a green city. Electric vehicles are becoming more popular around the world. In the USA, in 2022; people bought 800,000 new ones. The best American city for owners of electric cars in San Jose, California, which offers many electric charging stations.
Tạm dịch:
Những cách làm cho thành phố trở nên xanh
Làm thế nào chúng ta có thể cải thiện các thành phố nơi chúng ta sống? Hãy cùng tìm hiểu.
- Một trong những cách tốt nhất để cải thiện thành phố là thêm không gian xanh. Nông nghiệp đô thị rất phổ biến ở Paris, Pháp, nơi có khu vườn trên sân thượng lớn nhất thế giới. Người ta sử dụng nó để trồng thực phẩm tươi sống cho các nhà hàng và gia đình địa phương.
- Giảm việc sử dụng ô tô cũng rất quan trọng. Các thành phố như Auckland, New Zealand tạo ra những con đường an toàn khiến việc đi bộ trở thành lựa chọn tốt hơn lái xe. Amsterdam ở Hà Lan có hơn 500 km đường dành cho xe đạp.
- Xây dựng công trình xanh còn có thể cải thiện môi trường sống. Những tòa nhà này cải thiện chất lượng không khí cả bên trong và bên ngoài. Mọi người ít bị ốm hơn và có thể làm việc tốt hơn - họ thậm chí còn ngủ ngon hơn vào ban đêm vì các tòa nhà xanh sử dụng ánh sáng tự nhiên cả ngày. Adelaide ở Úc có nhiều công trình xanh.
- Giao thông sạch là điều cần thiết trong một thành phố xanh. Xe điện đang ngày càng trở nên phổ biến trên toàn thế giới. Ở Hoa Kỳ, vào năm 2022; người ta đã mua 800.000 cái mới. Thành phố tốt nhất của Mỹ dành cho chủ sở hữu ô tô điện ở San Jose, California, nơi có nhiều trạm sạc điện.
1. Read the text and decide if the statements (1-5) are R (right), W (wrong) or DS (doesn’t say).
(Đọc văn bản và quyết định xem các câu (1-5) là R (đúng), W (sai) hay DS (không nói).)
|
1. The biggest rooftop garden in the world is in Paris. |
|
|
2. There are nearly 500 kilometres of cycling paths in Amsterdam. |
|
|
3. Green buildings can improve sleep quality. |
|
|
4. Adelaide has got the most green buildings in Australia. |
|
|
5. There are lots of electric charging stations in San Jose. |
CÁC BÀI TẬP KHÁC