Giải SGK, SBT Unit 6. A multicutural world English Discovery
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 6 English Discovery
1. In groups, take the following quiz. Then check your answers with your partner.
(Làm bài tập sau theo nhóm. Sau đó kiểm tra câu trả lời của bạn với bạn cùng lớp.)
|
VOCABULARY FOCUS Multicultural societies (Xã hội đa văn hóa) assimilation indigenous culture (đồng hóa) (văn hóa bản địa) stereotype melting pot (khuôn mẫu) (nồi nóng chảy) cultural identity minority culture (bản sắc văn hóa) (văn hóa thiểu số) dominant culture. Multiculturalism (nền văn hóa thống trị) (chủ nghĩa đa văn hóa) |
1. What is multiculturalism?
(Đa văn hóa là gì?)
A. The belief that one culture is superior to others.
(Niềm tin rằng một nền văn hóa cao hơn những nền văn hóa khác.)
B. The idea that multiple cultures can coexist in a society.
(Ý tưởng cho rằng nhiều nền văn hóa có thể cùng tồn tại trong một xã hội.)
C. The idea of cultural assimilation in a country.
(Ý tưởng về sự đồng hóa văn hóa trong một quốc gia.)
2. Which of the following is an example of a typical stereotype?
(Điều nào sau đây là ví dụ về khuôn mẫu điển hình?)
A. A Vietnamese woman likes to wear traditional Áo dài
(Người phụ nữ Việt Nam thích mặc áo dài truyền thống)
B. An Asian student is often good at maths.
(Một học sinh châu Á thường giỏi toán.)
C. The sun rises in the east.
(Mặt trời mọc ở hướng Đông.)
3. What can be passed down to the next generation?
(Điều gì có thể truyền lại cho thế hệ sau?)
A. environmental pollution (ô nhiễm môi trường)
B. traditional crafts (nghề thủ công truyền thống)
C. natural disasters (thiên tai)
4. Which of the following is a traditional Japanese art form preserved until today?
(Loại hình nghệ thuật nào sau đây là loại hình nghệ thuật truyền thống của Nhật Bản được bảo tồn cho đến ngày nay?)
A. Origami (Nghệ thuật gấp giấy)
B. Water puppetry (Múa rối nước)
C. Calligraphy (Thư pháp)
5. In what way can a country embrace diverse cultural backgrounds of its citizens?
(Bằng cách nào một quốc gia có thể đón nhận nền tảng văn hóa đa dạng của người dân?)
A. Respect multiple cultures in the society
(Tôn trọng nhiều nền văn hóa trong xã hội)
B. Adopt stereotypes
(Chấp nhận những khuôn mẫu)
C. Allow the use of diverse musical instruments
(Cho phép sử dụng đa dạng các loại nhạc cụ)
6. Which of the following can shape a person's cultural identity?
(Điều nào sau đây có thể hình thành nên bản sắc văn hóa của một người?)
A. Language (ngôn ngữ)
B. Eye colour (màu mắt)
C. Occupation (nghề nghiệp)
7. Which of the following countries is often referred to as a 'melting pot'?
(Quốc gia nào sau đây thường được coi là “nồi nấu chảy”?)
A. Singapore
B. South Africa (Nam Phi)
C. United States (Hoa Kỳ)
8. Which country has a significant population of indigenous people?
(Quốc gia nào có dân số bản địa đáng kể?)
A. Mexico
B. Japan
C. Italy
3. Read the GRAMMAR FOCUS. Find and underline examples of As if/As though in the dialogue.
(Đọc TRỌNG TÂM NGỮ PHÁP. Tìm và gạch chân các ví dụ về As if/As though trong đoạn hội thoại.)
|
GRAMMAR FOCUS Adverbial clauses of manner Use as if and as though to talk about imaginary situations or situations that may not be true but are likely or possible. As if is more common than as though. As if / As though +S+V (present tense) It looks as if / as though it is going to rain. As if / As though +S+ were / V (simple past) He acts as if / as though he were Canadian. As if / as though often follow the verbs look feel, or seem |
|
NGỮ PHÁP TRỌNG TÂM Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ cách thức Sử dụng as if và as though để nói về những tình huống tưởng tượng hoặc những tình huống có thể không có thật nhưng có thể xảy ra hoặc có thể xảy ra. Như thể là phổ biến hơn như thể. Như thể / Như thể +S+V (thì hiện tại) Có vẻ như/như thể trời sắp mưa. Như thể / Như thể +S+ là / V (quá khứ đơn) Anh ấy hành động như thể/như thể anh ấy là người Canada. Như thể/như thể thường đi theo các động từ look, Feel, hoặc seem |
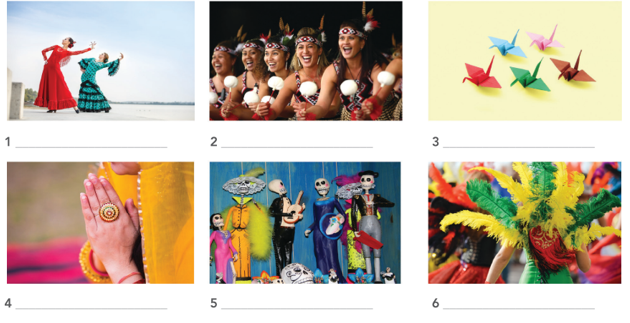
2. Label the photos with the names of the activities, customs, and objects.
(Dán nhãn cho các bức ảnh tên của các hoạt động, phong tục và đồ vật.)
|
Carnival Parade Day of the Dead (Cuộc diễu hành lễ hội) (Ngày của người chết) Flamenco Dance Haka Dance (Vũ điệu Flamenco) (Vũ điệu Haka) Origami Namaste |
3. Read the WRITING FOCUS and find examples of statistics in the sample essay.
(Đọc TRỌNG TÂM VIẾT và tìm các ví dụ về số liệu thống kê trong bài luận mẫu.)
|
WRITING FOCUS Giving statistics in essays has a number of ways: 1. Citing a source within the essay According to a recent survey by XYZ organization, 70% of respondents reported feeling stressed in a multicultural workplace. 2. Presenting the statistics in a table or graph following the essay As shown in Table 1, the number of employees facing discrimination in multinational companies has increased by 10% in the past five years. 3. Comparing two or more statistics While the number of women in management positions has increased by 20% in the past decade, the gender pay gap has only decreased by 5%. 4. Analyzing statistics over a period The unemployment rate in Việt Nam has steadily increased from 10% in 2010 to 14% in 2020. 5. Ranking According to the World Happiness. Report, Finland, Denmark, and Switzerland provide the top three happiest working environments in the world. |
|
TẬP TRUNG VIẾT Đưa ra số liệu thống kê trong bài luận có một số cách: 1. Trích dẫn nguồn trong bài luận Theo một cuộc khảo sát gần đây của tổ chức XYZ, 70% số người được hỏi cho biết họ cảm thấy căng thẳng ở nơi làm việc đa văn hóa. 2. Trình bày số liệu thống kê dưới dạng bảng hoặc biểu đồ sau bài luận Như trình bày trong Bảng 1, số lượng nhân viên bị phân biệt đối xử ở các công ty đa quốc gia đã tăng 10% trong 5 năm qua. 3. So sánh hai hoặc nhiều số liệu thống kê Trong khi số lượng phụ nữ ở các vị trí quản lý đã tăng 20% trong thập kỷ qua thì khoảng cách về lương giữa các giới chỉ giảm 5%. 4. Phân tích số liệu thống kê trong một khoảng thời gian Tỷ lệ thất nghiệp ở Việt Nam tăng đều đặn từ 10% năm 2010 lên 14% vào năm 2020. 5. Xếp hạng Theo Thế Giới Hạnh Phúc. Báo cáo, Phần Lan, Đan Mạch và Thụy Sĩ cung cấp ba môi trường làm việc hạnh phúc nhất thế giới. |
2. Complete the gaps with the given words / phrases in the box.
(Hoàn thành các chỗ trống với các từ/ cụm từ trong hộp.)
|
assimilation |
stereotype |
|
dominant culture |
indigenous culture |
|
melting pots |
minority cultures |
|
multiculturalism |
cultural identity |
1. In Viet Nam, the _____ of ethnic groups such as Dao, Mường, H’mông,... contribute to the cultural diversity of the whole country.
2. The _____ in Việt Nam is the culture of Kinh people as the majority of Vietnamese population is Kinh people.
3. Features such as gender, religion, social class, and language determine the _____ of a person.
4. _____ can be seen as a result of prolonged colonization, in which the native culture is gradually replaced by the culture of the colony.
5. In many Asian countries, there is a common _____ that men are the breadwinners of the families while women are full-time housewives.
6. The USA, the UK, and Australia can be seen as _____ of the world.
7. People from _____ practice unique traditions and retain social, cultural, economic, political characteristics that are distinct from those of dominant societies.
8. The main idea of _____ in a country refers to the existence of differences in terms of racial, ethnic, religious, and other cultural characteristics.
1. Complete the notes about adverbial clauses of manner with words in the box.
|
present |
possible |
|
|
common |
past |
verbs |
Adverbial clauses of manner
We use as if and as though to talk about two things:
• Imaginary situations
• Situations that may not be true but are likely or (1) _____
Structures of adverbial clauses of manner
• As if / As though + S + V ((2) _____ tense)
E.g.: He looks as though he is going to study in the US soon.
• As if / As though + S + V (simple (3) _____ tense)
E.g.: It seems as if many foreigners
appreciated Áo dài.
Note: As if is more (4) _____ than as though.
(5) _____ that often go after as if/ as though: look, feel, or seem
1. Fill in the blanks with the words given in the box.
(Điền vào chỗ trống với các từ cho trước trong hộp.)
|
green chillies |
garlic paste |
coriander |
|
tumeric |
garam masala |
ginger paste |

1. Complete the table using the words in the box.
|
pagoda visits |
Haka dance |
Kimono |
|
Carnival parade |
Namaste |
Origami |
|
Flamenco dance |
Hanbok |
Hong bao |
|
Activities |
Object |
2. Complete the gaps using the words / phrases in the box.
(Hoàn thành các chỗ trống dùng các từ trong hộp.)
|
treat everyone equally |
customary |
|
adopt cultural elements |
immigrants |
|
traditional outfit |
assimilate into |
|
special privileges |
1. The number of _____ from poor countries flocking to Germany is increasing rapidly.
2. Is it common in the USA that people from the dominant culture who _____ of the minority one in a disrespectful way?
3. To show cultural understanding, we need to _____ especially those from ethnic minority communities.
4. When moving to the USA, migrants are expected to _____ the American culture.
5. The _____ of Viet Nam is Áo dài.
6. In Scotland, it is _____ to wear Kilt in weddings or other formal occasions.
7. Minority groups in Viet Nam are in need of _____ from the government in order to have more opportunities to thrive.
1. Match the phrases to their meanings.
(Nối các cụm từ với nghĩa của chúng.)
|
1. deal with 2. engage in 3. figure out 4. substitute for 5. provide for |
a. to give someone the things they need b. to perform the same job as another thing or person or to take their place c. to handle d. to take part in e. to finally understand something or someone, or find the solution to a problem after a lot of thought |
2. Complete the gaps using the prepositions in the box.
(Hoàn thành các chỗ trống dùng các giới từ trong hộp.)
|
about |
in |
out |
for |
on |
with |
1. It is important to sort the problems _____ when arguments among family members occur in order to know the root of the conflict.
2. As an enthusiast in cultural studies, Yến wants to apply _____ a job in an organization that advocates for cultural diversity preservation.
3. It is a common cultural practice that many Vietnamese parents always check _____ their children every day via phone call when they study far from family.
4. To communicate _____ people from ethnic minority groups in Việt Nam is now much easier than a couple of years ago.
5. Governments worldwide should invest _____ preserving cultural sites and traditional beauty of their countries.
6. Native people of many melting pot societies care a lot _____ the potential threats that vast immigration might cause to their life.
3. Complete the text with the correct form of the given verbs from the box.
(Hoàn thành bài đọc với dạng đúng của động từ cho trước từ trong hộp.)
|
participate |
disagree |
cope |
find |
|
specialize |
account |
argue |
worry |
In Việt Nam, many people choose to marry foreigners which (1) _____ for an increasing number of multicultural families these days. There are certain pros and cons of living in this type of family. On the one hand, children of multicultural families usually do not have to (2) _____ about traveling as they have two or ever more nationalities. Besides, they have a chance to (3) _____ in educational programs in bilingual schools al a very early age as they (4) _____ in leaching languages to bilingual kids. On the other hand, conflicts can also occur daily in a multicultural family. Due to language barriers, members of a multicultural family (5) _____ with each other very frequently. They might have strong conflicts and (6) _____ on a lot of things such as behaviors, opinions, beliefs and practices. Parents of these families also need to (7) _____ with challenges in bringing up the kids in a culturally diverse environment. As a member of a multicultural
family, I did (8) _____ out an effective solution to this issue, which is to hold occasional family gatherings in order to understand each other more.










