Câu hỏi
Cho hai hàm số \(y = \dfrac{{x - 1}}{x} + \dfrac{x}{{x + 1}} + \dfrac{{x + 1}}{{x + 2}} + \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}}\) và \(y = \left| {x + 2} \right| - x - m\) (\(m\) là tham số thực) có đồ thị lần lượt là \(\left( {{C_1}} \right)\) và \(\left( {{C_2}} \right)\) cắt nhau tại đúng bốn điểm phân biệt là
- A \(\left[ { - 2; + \infty } \right)\)
- B \(\left( { - \infty ; - 2} \right)\)
- C \(\left( { - 2; + \infty } \right)\)
- D \(\left( { - \infty ; - 2} \right]\)
Phương pháp giải:
- Biến đổi phương trình về \( - m = f\left( x \right)\).
- Xét hàm \(y = f\left( x \right)\) và sử dụng mối quan hệ giữa số nghiệm của phương trình với số giao điểm của đồ thị hàm số với đường thẳng tìm \(m\).
Lời giải chi tiết:
Xét phương trình hoành độ giao điểm:
\(\begin{array}{l}\dfrac{{x - 1}}{x} + \dfrac{x}{{x + 1}} + \dfrac{{x + 1}}{{x + 2}} + \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}} = \left| {x + 2} \right| - x - m\\ \Leftrightarrow \dfrac{{x - 1}}{x} + \dfrac{x}{{x + 1}} + \dfrac{{x + 1}}{{x + 2}} + \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}} - \left| {x + 2} \right| + x = - m\end{array}\)
Xét \(f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 1}}{x} + \dfrac{x}{{x + 1}} + \dfrac{{x + 1}}{{x + 2}} + \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}} - \left| {x + 2} \right| + x\) trên \(D = \mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ { - 3; - 2; - 1;0} \right\}\).
+) Xét trên \({D_1} = \left( { - \infty ; - 2} \right)\backslash \left\{ { - 3} \right\}\) thì \(f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 1}}{x} + \dfrac{x}{{x + 1}} + \dfrac{{x + 1}}{{x + 2}} + \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}} + 2x + 2\)
Có \(f'\left( x \right) = \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 1} \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 2} \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 3} \right)}^2}}} + 2 > 0,\forall x \in {D_1}\) nên hàm số đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left( { - \infty ; - 3} \right)\) và \(\left( { - 3; - 2} \right)\).
+) Xét trên \({D_2} = \left( { - 2; + \infty } \right)\backslash \left\{ { - 1;0} \right\}\) thì \(f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 1}}{x} + \dfrac{x}{{x + 1}} + \dfrac{{x + 1}}{{x + 2}} + \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}} - 2\)
Có \(f'\left( x \right) = \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 1} \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 2} \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {x + 3} \right)}^2}}} > 0,\forall x \in {D_2}\) nên hàm số đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left( { - 2; - 1} \right),\left( { - 1;0} \right)\) và \(\left( {0; + \infty } \right)\).
\(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to + \infty } f\left( x \right) = 2;\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - \infty } f\left( x \right) = - \infty \); \(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - {3^ + }} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - {2^ + }} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - {1^ + }} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} f\left( x \right) = - \infty \);
\(\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - {3^ - }} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - {2^ - }} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to - {1^ - }} f\left( x \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} f\left( x \right) = + \infty \).
Bảng biến thiên:
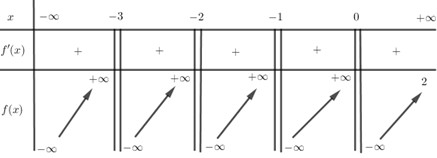
Quan sát bảng biến thiên ta thấy, phương trình \( - m = f\left( x \right)\) có bốn nghiệm phân biệt \( \Leftrightarrow - m \ge 2 \Leftrightarrow m \le - 2\).
Vậy \(m \in \left( { - \infty ; - 2} \right]\).
Chọn D.







